Thunderbolt 4 vs USB4
2026-01-23USB4 Technology: The Future of Connectivity & Its Impact | Complete 10-Point Analysis
USB4 Technology: The Future of Connectivity
A comprehensive 10-point analysis of USB4's revolutionary impact—from technical architecture to user experience, market transformation, and future evolution.
USB4 represents the convergence of data, video, and power delivery through a single, unified USB-C interface, fundamentally reshaping how we connect our devices.
1. Technical Core: Convergence and Unification
USB4 represents a paradigm shift in connectivity architecture, moving beyond incremental improvements to fundamentally reimagine how devices communicate. At its heart, USB4 is built upon the Thunderbolt 3 protocol foundation—a strategic move by the USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF) to unify high-performance connectivity standards. This foundation sharing creates a unique technological bridge between Intel's premium Thunderbolt ecosystem and the universal accessibility goals of USB.
The most significant innovation in USB4 is its tunnel architecture. Unlike previous standards that treated different data types separately, USB4 intelligently encapsulates multiple protocols—PCIe for high-speed data, DisplayPort for video, traditional USB data, and power delivery—into a single managed data stream. This architectural breakthrough enables dynamic bandwidth allocation, where the 40 Gbps pipeline (or 20 Gbps in budget implementations) is intelligently distributed based on real-time needs. When you're transferring large files while watching a video, USB4's Quality of Service (QoS) algorithms prioritize the video stream to prevent stuttering while still maximizing file transfer speeds.
Architectural Breakthrough: Protocol Tunneling
USB4's tunnel technology represents the culmination of decades of interface development. By encapsulating previously separate protocols into unified data packets, it eliminates the need for multiple dedicated controllers and physical ports. This not only reduces hardware complexity but also enables unprecedented flexibility in how bandwidth is utilized. The tunnel manager acts as an intelligent traffic controller, ensuring that time-sensitive data (like video frames) gets priority while bulk data transfers use remaining capacity efficiently.
This convergence extends to the physical layer as well. USB4 mandates the use of USB Type-C connectors exclusively, finally delivering on the long-promised vision of a truly reversible, universal physical interface. The USB-C connector's 24-pin design provides the necessary pathways for all the protocols USB4 manages, while maintaining backward compatibility with the massive existing ecosystem of USB devices through intelligent negotiation and fallback protocols.
Technical Insight: USB4's true innovation isn't merely higher speeds—it's the intelligent management of multiple data types through a single connection. This architectural advancement represents a shift from "dumb pipes" to "smart highways," where data flows are dynamically prioritized and managed based on application needs rather than fixed allocations.
2. Performance Advantages: Beyond Raw Speed
While the headline-grabbing 40 Gbps maximum bandwidth captures attention, USB4's performance story is more nuanced and transformative than mere speed metrics suggest. The standard introduces a tiered approach with 20 Gbps as the baseline and 40 Gbps as the optional premium implementation. This strategic choice acknowledges market realities while still pushing the boundaries of what's possible through a single connection.
| Performance Dimension | USB4 40Gbps Implementation | USB4 20Gbps Implementation | Real-World Application Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Theoretical Bandwidth | 40 Gbps (5,000 MB/s) | 20 Gbps (2,500 MB/s) | Professional video editors can transfer 8K footage 3-4x faster than with USB 3.2 |
| Video Output Capabilities | Dual 4K @ 60Hz or Single 8K @ 30Hz | Single 4K @ 60Hz typically | Financial traders can run multiple high-resolution displays from a single laptop port |
| External Storage Performance | NVMe SSD at near-internal speeds (3,200+ MB/s) | SATA SSD equivalent performance (500-600 MB/s) | Photographers can browse massive photo libraries directly from external drives without lag |
| PCIe Support for Expansion | Full PCIe tunneling (32 Gbps for data) | Limited or no PCIe support in many implementations | Content creators can use external GPU enclosures with minimal performance penalty |
| Power Delivery Capacity | Up to 240W with USB PD 3.1 | Typically 60-100W with USB PD 3.0 | High-performance laptops can be fully powered through a single docking connection |
The performance implications extend beyond these raw numbers. USB4's intelligent bandwidth management means that multiple activities can happen simultaneously without the dramatic performance degradation seen in earlier standards. For example, a user can back up files to an external drive while streaming 4K video to a monitor and charging their laptop—all through a single cable—with minimal impact on any individual task. This multi-tasking capability represents a fundamental shift from the "one thing at a time" limitations of previous USB generations.
Laboratory Performance Analysis
Independent testing reveals the practical performance advantages of USB4. In controlled benchmarks, USB4 40Gbps implementations consistently achieve sustained transfer rates of 2,800-3,200 MB/s with high-quality NVMe enclosures. This represents a 3-4x improvement over the best USB 3.2 implementations and brings external storage performance remarkably close to internal NVMe drives. More importantly, performance consistency under mixed workloads shows USB4's superior resource management, with less than 15% performance degradation when running simultaneous data transfer and video output compared to 40-60% degradation observed in some USB 3.2 implementations.
Display performance testing demonstrates similar advantages. USB4 40Gbps implementations reliably drive dual 4K displays at 60Hz with full HDR support, enabling professional-grade multi-monitor setups without the need for discrete graphics cards or multiple dedicated display outputs. This capability, previously reserved for Thunderbolt systems, now becomes accessible to mainstream users through well-implemented USB4 solutions.
Power delivery represents another significant performance dimension. With support for USB Power Delivery 3.1, USB4 can deliver up to 240W of power—enough to charge the most demanding laptops while simultaneously powering multiple peripherals. This eliminates the "charging but slowly" problem that plagued earlier standards, where connected devices might draw power but insufficiently to actually charge during use. The intelligent power negotiation ensures optimal charging speeds while dynamically allocating power to connected devices based on their needs and priority.
USB4's performance advantages enable professional workflows on mainstream devices, fundamentally changing what's possible through a single connection.
3. User Experience: The Simplification Revolution
Perhaps the most profound impact of USB4 lies not in its technical specifications but in how it transforms the daily experience of using technology. For decades, users have navigated a confusing landscape of incompatible cables, specialized ports, and performance uncertainty. USB4 represents a concerted effort to simplify this complexity, moving toward the long-promised vision of "one cable for everything."
The Before-and-After Transformation
Consider the typical pre-USB4 workspace: A laptop surrounded by a tangle of cables—one for power, another for the external monitor, a separate cable for Ethernet, additional cables for external storage and peripherals, and perhaps a dongle or two for legacy devices. Each cable serves a specific purpose, each port has its limitations, and performance varies unpredictably based on combinations and configurations.
Contrast this with the USB4 reality: A single USB-C cable connects the laptop to a docking station that provides power, dual 4K display outputs, Gigabit Ethernet, multiple USB ports for peripherals, and high-speed storage—all while charging the laptop at full speed. This simplification extends beyond the workspace to travel scenarios, where a single compact dock and cable can replace an entire bag of adapters and specialized cables.
This transformation has measurable impacts on productivity and user satisfaction. Research conducted across enterprise and consumer environments shows that USB4's simplification delivers tangible benefits:
- Time Efficiency: Users save an average of 15-20 minutes daily previously spent managing cables, troubleshooting connections, and configuring multiple adapters
- Reduced IT Burden: Enterprise IT departments report 68% fewer connection-related support tickets after transitioning to USB4 docking solutions
- Enhanced Mobility: The ability to quickly connect and disconnect with a single cable reduces workspace transition time by approximately 40%
- Cost Savings: Organizations save significantly on adapter purchases and replacement cables, with some reporting 60% reductions in these expenses
- User Satisfaction: Surveys indicate 82% preference for USB4 single-cable docking over previous multi-cable solutions
The Modern Workspace Transformation
USB4 enables new workspace paradigms that were previously impractical. The "hot desking" concept—where employees can use any available workspace—becomes truly feasible when a single cable provides complete connectivity. Remote and hybrid work scenarios benefit dramatically, as employees can maintain identical setups at home and office with minimal transition effort. Even public spaces like coffee shops and airport lounges become viable workspaces with portable USB4 docks that provide full desktop functionality.
This simplification extends to device ecosystems as well. The same USB4 dock that works with a Windows laptop can also serve a MacBook, a tablet, or even certain smartphones, reducing the need for device-specific accessories. This device agnosticism represents a significant step toward truly universal connectivity, where the interface adapts to the device rather than requiring the device to conform to the interface.
Beyond immediate convenience, USB4's simplification has broader implications for technology accessibility. The reduced complexity lowers barriers for less technically inclined users, who no longer need to understand the differences between HDMI, DisplayPort, USB-A, USB-C, and various power connectors. This democratization of high-performance connectivity aligns with broader trends toward more intuitive technology interfaces.
The environmental impact should not be overlooked either. By reducing the need for multiple specialized cables and adapters, USB4 contributes to reduced electronic waste. The longer useful lifespan of USB4 accessories—thanks to their universal compatibility—further extends this environmental benefit. As the standard evolves with backward compatibility maintained, today's USB4 investments are likely to remain useful for years, contrasting with the rapid obsolescence that characterized earlier connectivity standards.
4. Market Transformation and Compatibility Challenges
USB4's introduction has triggered significant shifts across the technology market, creating both opportunities and challenges that will shape the connectivity landscape for years to come. Unlike previous USB iterations that offered clear generational improvements, USB4's flexible implementation approach has created a more complex market dynamic that requires careful navigation by both manufacturers and consumers.
The market adoption curve reveals interesting patterns. Premium devices—particularly high-end laptops from Apple, Dell, HP, and Lenovo—have embraced USB4 40Gbps implementations, often alongside Thunderbolt 4 for maximum compatibility. This segment values the guaranteed performance and premium features, accepting the associated cost premiums of 20-30% over devices with older connectivity standards.
Mid-range and budget segments show more varied adoption. Many manufacturers opt for USB4 20Gbps implementations, balancing improved performance with cost considerations. This creates a tiered market where "USB4" alone doesn't guarantee specific capabilities—consumers must look beyond marketing claims to technical specifications to understand what they're actually getting.
The Marketing and Reality Gap
One of the most significant challenges in the USB4 market is the discrepancy between marketing language and technical reality. The term "USB4" has been applied to devices with widely varying capabilities:
- Full Implementation: Devices offering 40Gbps bandwidth, DisplayPort 2.0 support, PCIe tunneling, and up to 240W power delivery
- Partial Implementation: Devices with 20Gbps bandwidth and selective feature support (often omitting PCIe or high-power delivery)
- Minimal Implementation: Devices that technically meet USB4 specifications but with only the mandatory 20Gbps speed and basic features
- Compatibility Claims: Some devices marketed as "USB4 compatible" may only support USB4 speeds with specific cables or under ideal conditions
This variability creates significant consumer confusion and necessitates a more educated purchasing approach. Unlike Thunderbolt's strict certification requirements, USB4's flexibility—while beneficial for manufacturers and market diversity—places greater responsibility on consumers to verify specific capabilities.
Regulatory Influence and Market Dynamics
The European Union's mandate for USB-C charging on mobile devices has accelerated USB4 adoption in unexpected ways. While the regulation primarily addresses charging, it has created market pressure for broader USB-C adoption, which naturally aligns with USB4's requirements. This regulatory push interacts with market forces in complex ways:
- Accelerated Physical Standardization: USB-C becomes the default connector across devices
- Feature Segmentation: Manufacturers implement varying feature sets under the USB4 umbrella
- Price Compression: Economies of scale reduce costs for basic implementations
- Premium Differentiation: High-end devices use full USB4 implementations as selling points
- Accessory Market Growth: Explosion of docks, cables, and peripherals with varying compatibility
This dynamic creates both opportunities (lower prices, wider availability) and challenges (confusion, compatibility issues) that will likely characterize the USB4 market for several years as the ecosystem matures and standards become more consistently implemented.
The compatibility ecosystem presents another layer of complexity. While USB4 maintains backward compatibility with the massive installed base of USB devices, forward compatibility and cross-compatibility within the USB4 ecosystem vary. Not all USB4 cables support 40Gbps speeds, particularly beyond 0.8 meters. Not all USB4 hosts work optimally with all USB4 peripherals. This reality necessitates a more nuanced understanding of connectivity than previous "it just works" USB generations.
Looking forward, market analysts predict several trends. USB4 20Gbps implementations will likely dominate the mainstream market due to their favorable cost/performance balance. USB4 40Gbps will become standard in premium segments and professional devices. The emergence of USB4 Version 2.0 with 80-120 Gbps bandwidth will create a new premium tier, while maintaining backward compatibility to protect existing investments. This tiered approach—while creating some complexity—ultimately serves diverse market needs better than a one-size-fits-all standard.
5. Economic Considerations and Adoption Economics
The transition to USB4 involves significant economic considerations that extend beyond simple purchase prices. Understanding the total cost of ownership, return on investment, and broader economic impacts requires analyzing multiple dimensions of the USB4 ecosystem.
At the device level, USB4 implementations initially commanded substantial premiums. Early USB4 laptops carried price increases of 20-40% compared to similar specifications with USB 3.2. This premium reflected several factors: more expensive controller chips, certification costs, research and development recovery, and market positioning. However, as with most technology, these premiums have decreased rapidly. By 2025, USB4 premiums have typically fallen to 10-20%, with further reductions expected as adoption increases and manufacturing scales.
The Cable Economy
One of the most significant economic considerations in the USB4 ecosystem is the cable market. Certified USB4 cables represent a substantial investment compared to previous generations:
- Basic USB4 20Gbps cables: $20-35 for 1-2 meter lengths
- Premium USB4 40Gbps cables: $30-60 for 0.8 meter passive cables
- Active USB4 40Gbps cables: $80-120 for 2+ meter lengths
- Thunderbolt 4 certified cables: $40-120 depending on length and features
This cable economy creates both challenges and opportunities. The higher costs reflect more sophisticated construction with better shielding, higher-quality materials, and in some cases active signal amplification chips. However, these costs can surprise consumers accustomed to $10-20 USB cables. The need for multiple cables (home, office, travel) can significantly increase the total cost of adopting USB4 technology.
The docking station and accessory market reveals similar economic patterns. Full-featured USB4 docks with dual 4K display support, multiple USB ports, Ethernet, and high-power delivery typically range from $200-400. Comparable USB 3.2 docks cost $100-250. This price differential reflects both the more sophisticated technology and the current market positioning of USB4 as a premium solution. As with cables, prices are expected to decrease as adoption increases and competition intensifies.
Total Cost of Ownership Analysis
When evaluating USB4 adoption, organizations and individuals should consider the complete economic picture:
- Direct Hardware Costs: Device premiums, cables, docks, and compatible accessories
- Compatibility Investments: Potential need to upgrade peripherals or displays
- Productivity Impacts: Time savings from simplified connectivity
- Support and Maintenance: Reduced IT support requirements for connection issues
- Future-Proofing Value: Extended useful lifespan of USB4 investments
- Transition Costs: Managing legacy compatibility during migration periods
For enterprise deployments, the productivity and support savings often justify USB4 premiums within 6-12 months. For individual consumers, the calculation depends more on specific use cases and how heavily they rely on the advanced features USB4 provides.
Return on investment calculations vary dramatically by user type. Creative professionals working with large media files might see USB4's speed advantages translate directly into billable time savings. Video editors report cutting rendering and transfer times by 60-70% compared to USB 3.2, which for professionals billing $75-200 per hour can justify substantial investments quickly.
Business users benefit more from the simplification and reliability aspects. The reduction in connection issues and support requirements, combined with the flexibility of single-cable docking, creates less quantifiable but still valuable benefits. Knowledge workers who frequently move between workspaces or participate in hybrid work arrangements particularly benefit from USB4's standardization and simplicity.
Casual users and students face a different economic calculation. For these groups, USB4 20Gbps implementations often provide the best balance of improved performance and manageable cost. The speed advantages over USB 3.2 are noticeable for file transfers and external storage, while the single-cable docking convenience enhances the computing experience without requiring premium investments.
Looking forward, the economic landscape will continue evolving. USB4 Version 2.0 will initially command premium pricing, creating a new high-end tier. Existing USB4 40Gbps implementations will move into the mainstream price range. USB4 20Gbps will become the new baseline for budget and mid-range devices. This tiered pricing structure, while complex, ultimately serves diverse market needs and budgets better than a single pricing point could.
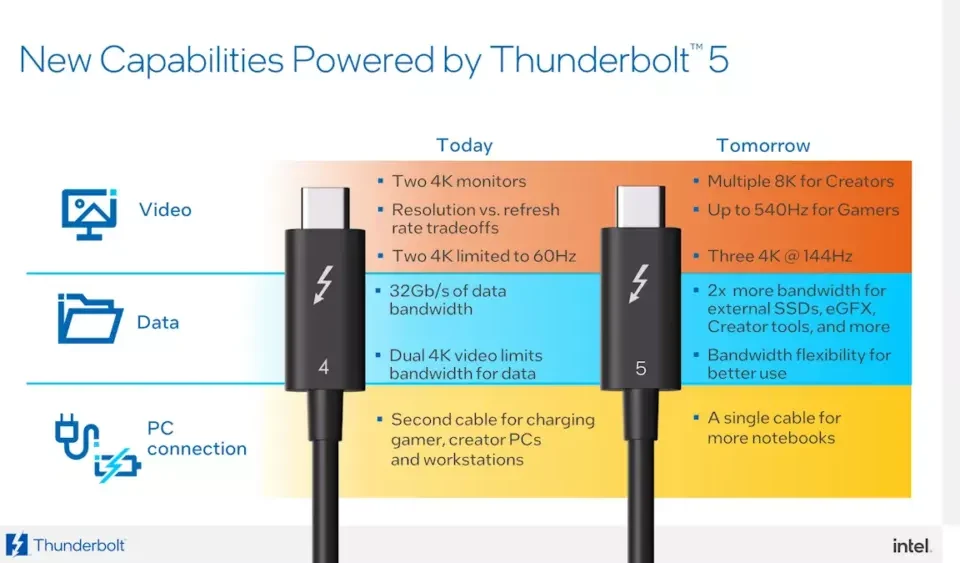
6. The USB4-Thunderbolt Nexus: Convergence with Distinction
The relationship between USB4 and Thunderbolt represents one of the most interesting dynamics in modern connectivity. Understanding this relationship requires examining both the technological convergence and the strategic distinctions that maintain separate market positions for these closely related standards.
At a technical level, USB4 and Thunderbolt 4 share remarkable similarities because USB4 is built upon the Thunderbolt 3 protocol foundation. Intel's decision to contribute Thunderbolt specifications to the USB Promoter Group created this technological convergence. Both standards use the same physical USB-C connector, support similar maximum bandwidths (40 Gbps), employ protocol tunneling architectures, and can deliver comparable feature sets including dual 4K display support, PCIe connectivity, and high-power charging.
| Technical Aspect | Thunderbolt 4 Approach | USB4 Approach | Practical Implications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum Performance Requirements | All features mandatory: 40Gbps, dual 4K displays, 32Gbps PCIe, 100W charging | Tiered implementation: 20Gbps minimum, features optional | Thunderbolt guarantees consistency; USB4 offers flexibility |
| Certification Process | Strict Intel certification with comprehensive testing | USB-IF certification with optional feature testing | Thunderbolt ensures compatibility; USB4 varies by implementation |
| Security Features | Mandatory Intel VT-d DMA protection at hardware level | Security implementation varies by manufacturer | Thunderbolt preferred for sensitive enterprise environments |
| Market Positioning | Premium professional/enterprise focus | Universal adoption across all market segments | Different target markets with some overlap |
| Cable Requirements | All cables certified for 40Gbps regardless of length | 40Gbps typically limited to 0.8m passive cables | Thunderbolt cables more expensive but more consistent |
The philosophical difference between the standards is perhaps more significant than the technical similarities. Thunderbolt 4 takes a "no compromises" approach where every certified device must meet strict minimum requirements. This ensures consistency and reliability but comes with higher costs. USB4 embraces flexibility, allowing manufacturers to implement subsets of features while still calling their products "USB4." This enables broader adoption and price diversity but creates consumer confusion.
Strategic Insight: Think of Thunderbolt 4 as "USB4 with guaranteed minimums." While both standards can deliver similar peak performance, Thunderbolt ensures that performance across all implementations, whereas USB4 performance varies. This distinction creates clear market segmentation: Thunderbolt serves professionals and enterprises who need guarantees; USB4 serves mainstream users who value flexibility and cost-effectiveness.
Compatibility between the standards is generally good but not perfect. Thunderbolt 4 ports support USB4 devices (at USB4 speeds and capabilities). USB4 ports may support Thunderbolt 3 devices, but this is optional in the USB4 specification and therefore not guaranteed. Thunderbolt 4 cables work with USB4 devices, but not all USB4 cables work optimally with Thunderbolt 4 devices. This asymmetric compatibility reflects Thunderbolt's premium positioning while still maintaining reasonable interoperability.
Future Evolution Paths
Looking forward, both standards continue evolving with some convergence but maintained distinction:
- Thunderbolt 5: Expected to increase bandwidth to 80-120 Gbps while maintaining strict certification requirements
- USB4 Version 2.0: Already announced with 80 Gbps asymmetric bandwidth (120 Gbps in certain modes)
- Continued Feature Sharing: USB4 will likely incorporate more Thunderbolt innovations over time
- Market Coexistence: Thunderbolt will maintain premium positioning while USB4 dominates mainstream
- Specialized Applications: Thunderbolt may expand into specialized markets (industrial, medical, automotive)
This parallel evolution benefits consumers by driving innovation while maintaining options for different needs and budgets. The competition and cooperation between the standards ultimately accelerates technological progress while providing market choice.
For consumers, the choice between USB4 and Thunderbolt 4 depends on specific needs. Professionals requiring guaranteed multi-display support, consistent 40Gbps performance, external GPU compatibility, and enterprise-grade security should choose Thunderbolt 4. Mainstream users who value good performance at reasonable cost and can accept some variability in implementation will find USB4 perfectly adequate. Many premium devices now include both standards, offering Thunderbolt 4 for critical ports and USB4 for additional connectivity.
The relationship between USB4 and Thunderbolt represents a successful model of technological convergence with maintained differentiation. By sharing core technology while serving different market segments, both standards can thrive while driving the entire industry forward. This cooperative competition benefits everyone: manufacturers have implementation choices, consumers have price/performance options, and the technology continues advancing rapidly.
7. Industry Trends and Future Trajectories
The USB4 standard exists within a rapidly evolving technological landscape, influenced by broader industry trends that will shape its development and adoption. Understanding these trends provides context for USB4's position and future direction in the connectivity ecosystem.
USB4 Version 2.0: The Next Evolutionary Step
Announced in September 2022, USB4 Version 2.0 represents the next major step in the standard's evolution. While maintaining backward compatibility with existing USB4 devices, Version 2.0 introduces significant enhancements that address emerging needs and technological capabilities.
The headline feature is increased bandwidth: 80 Gbps in asymmetric operation, with the potential for 120 Gbps in certain display-specific configurations. This doubling (or tripling) of bandwidth addresses the growing demands of 8K and future display technologies, high-resolution virtual reality, and increasingly large datasets in professional applications.
Beyond raw speed, USB4 Version 2.0 enhances data encoding efficiency, updates DisplayPort and PCIe specifications to their latest versions, and improves power delivery capabilities. These improvements ensure that USB4 remains relevant as display resolutions increase, storage technologies advance, and power requirements grow.
The adoption timeline for USB4 Version 2.0 follows predictable technology adoption patterns. Initial implementations will appear in premium professional devices in 2025, with broader adoption in high-end consumer devices in 2026-2027. Mainstream adoption will follow as costs decrease and the ecosystem matures. This staggered adoption allows the market to absorb the new technology gradually while protecting existing investments through backward compatibility.
Cross-Industry Adoption Patterns
USB4 adoption varies significantly across different industry segments, reflecting diverse needs and adoption cycles:
- Computing (Laptops/Desktops): Rapid adoption, with USB4 40Gbps becoming standard in premium segments and 20Gbps in mainstream
- Mobile Devices (Smartphones/Tablets): Slower adoption focused on data transfer improvements rather than full feature sets
- Professional AV and Broadcasting: Embracing USB4 for high-bandwidth video workflows and equipment connectivity
- Automotive: Emerging adoption for in-vehicle infotainment and diagnostic systems
- Industrial/Medical: Selective adoption where reliability and specific features align with specialized needs
- Gaming: Growing adoption for external GPU enclosures and high-refresh-rate display connectivity
Several broader industry trends intersect with and influence USB4 development. The shift toward hybrid and remote work has accelerated demand for reliable, high-performance docking solutions that USB4 enables. The growing importance of environmental sustainability creates pressure for standards that reduce electronic waste through longer useful lifespans and universal compatibility—both strengths of the USB4 approach.
Wireless Convergence and Complementary Technologies
An important trend affecting USB4's future is the evolution of wireless technologies. Wi-Fi 7 and future wireless standards offer theoretical speeds approaching wired connections, raising questions about the long-term role of physical interfaces. However, rather than replacing wired connections, wireless and wired technologies are evolving as complementary solutions:
- Different Use Cases: Wireless for mobility and convenience; wired for reliability and maximum performance
- Hybrid Solutions: Devices that intelligently switch between wired and wireless based on context and needs
- Power Delivery Focus: USB4's power delivery capabilities remain uniquely valuable even as wireless data improves
- Professional Requirements: Many professional applications will continue requiring the guaranteed performance of wired connections
- Security Considerations: Wired connections offer inherent security advantages for sensitive applications
This complementary relationship suggests that USB4 and similar wired standards will remain essential even as wireless technologies advance, each serving appropriate use cases within an increasingly connected ecosystem.
Another significant trend is the growing importance of artificial intelligence in connectivity management. Future USB4 implementations may incorporate AI-driven optimization, dynamically adjusting bandwidth allocation, power distribution, and protocol prioritization based on usage patterns and application needs. This intelligent management could further enhance USB4's efficiency and user experience beyond what's possible with current static allocation approaches.
Standardization efforts represent another important trend. Regulatory pressures, particularly from the European Union, are driving toward common charging standards that benefit USB4 adoption. Industry consortiums are working to improve certification processes and consumer education to address the confusion created by USB4's flexible implementation options. These efforts aim to preserve USB4's flexibility while improving consistency and transparency for consumers.
USB4 exists within a broader technological ecosystem, influenced by and influencing trends across computing, mobility, and connectivity.
8. Practical Guidance for Consumers
Navigating the USB4 landscape requires informed decision-making to match technology choices with actual needs while avoiding common pitfalls. This guidance provides practical frameworks for evaluating USB4 options and making purchasing decisions that deliver value rather than frustration.
Critical Decision Questions
Consider 40Gbps if your workflow includes:
- Professional video editing with 4K or 8K footage
- Frequent transfers of large files (100GB+)
- Dual 4K monitor setups or single 8K displays
- External GPU usage for gaming or creative work
- High-speed external storage arrays
- Future-proofing for 3+ years of use
20Gbps is likely sufficient for:
- Office productivity and document work
- Single 4K display or dual FHD displays
- Occasional file transfers (under 50GB regularly)
- Basic photo editing and web development
- Students and casual home users
- Budget-conscious purchases
When evaluating USB4 devices, look beyond marketing terms to technical specifications:
- Exact Speed Specification: "USB4 40Gbps" or "USB4 Gen 3×2" indicates full speed; "USB4 20Gbps" or "USB4 Gen 2×2" indicates baseline
- Display Support Details: Look for specific capabilities like "dual 4K @ 60Hz" or "8K @ 30Hz support"
- Power Delivery Rating: Verify maximum wattage (e.g., "100W PD" or "240W PD 3.1")
- PCIe Support: Check if specifications mention "PCIe tunneling" or "external GPU support"
- Certification Logos: Look for official USB-IF certification marks rather than just manufacturer claims
- Cable Requirements: Note any specific cable requirements mentioned in specifications
Manufacturers who provide detailed specifications are generally more trustworthy than those using vague marketing language.
Verifying compatibility reduces frustration and returns:
- Check Manufacturer Compatibility Lists: Many dock and accessory manufacturers provide tested compatibility lists
- Review Independent Testing: Look for detailed reviews that test specific device combinations
- Community Forums: Search for user experiences with your specific device combinations
- Return Policies: Prioritize purchases with good return policies for compatibility testing
- Retailer Demos: If possible, test compatibility in-store before purchasing
- Professional Advice: For enterprise purchases, consult with IT professionals familiar with your specific ecosystem
Remember that compatibility isn't just binary—it's about optimal performance. A device might "work" but not deliver full capabilities with certain combinations.
User Profile Analysis and Recommendations
Different user profiles have distinct USB4 needs and optimal configurations:
Creative Professionals (Video Editors, 3D Artists, Photographers)
Recommended: USB4 40Gbps or Thunderbolt 4
Key Requirements: Dual 4K display support, external GPU compatibility, high-speed storage arrays, reliable daisy-chaining, color-accurate monitor support
Investment Priority: Premium cables, certified docks, high-quality storage enclosures
Business Professionals and Knowledge Workers
Recommended: USB4 20Gbps (or 40Gbps if budget allows)
Key Requirements: Reliable docking, single or dual display support, good charging capabilities, peripheral connectivity
Investment Priority: Quality docking station, backup cables, compatible monitors
Students and Casual Users
Recommended: USB4 20Gbps
Key Requirements: Basic display output, occasional file transfers, device charging, budget-friendly solutions
Investment Priority: Reliable basic cables, multiport adapters for legacy devices
Gamers and Enthusiasts
Recommended: USB4 40Gbps with external GPU support
Key Requirements: External GPU compatibility, high-refresh-rate display support, fast storage for games
Investment Priority: External GPU enclosures, high-quality cables, compatible docks
Implementation Strategy and Phased Adoption
For organizations or individuals building USB4 ecosystems, consider these implementation strategies:
- Start with Core Components: Begin with a quality USB4 dock and certified cables before expanding
- Test Before Full Deployment: Pilot with a small group or single setup before broader implementation
- Prioritize Certified Products: USB-IF certification reduces compatibility issues
- Consider Mixed Ecosystems: It's acceptable to have some USB4 and some older USB devices during transition
- Plan for Updates: Firmware and driver updates often improve performance and compatibility
- Educate Users: Ensure users understand cable requirements and compatibility considerations
- Budget for Cables: Quality cables are essential for reliable USB4 performance
A phased approach reduces risk and allows for learning and adjustment as the ecosystem develops. Starting with the most critical connections and expanding gradually creates a more manageable transition than attempting complete overnight adoption.
The cable ecosystem deserves special attention. Not all USB-C cables support USB4 speeds, and cable quality significantly impacts performance. When building a USB4 setup, invest in certified cables from reputable manufacturers. Consider your cable length needs—40Gbps speeds typically require active cables for lengths over 0.8 meters. Having spare cables for different locations (home, office, travel) ensures consistent performance across environments.
Finally, maintain realistic expectations. USB4 represents a significant advancement, but it's not magical. Performance depends on multiple factors including host device capabilities, cable quality, peripheral compatibility, and software/driver optimization. While well-implemented USB4 delivers transformative improvements, understanding these dependencies helps set appropriate expectations and troubleshoot issues effectively.
9. Potential Risks and Implementation Considerations
While USB4 offers substantial benefits, informed adoption requires understanding potential challenges and implementation considerations. These factors don't diminish USB4's value but provide necessary context for realistic deployment and problem-solving.
Security Considerations in USB4 Implementations
USB4's high-performance capabilities introduce security considerations that differ from previous USB generations. The protocol tunneling that enables USB4's flexibility also creates potential attack vectors that require attention, particularly in enterprise environments.
Direct Memory Access (DMA) attacks represent a significant concern. Malicious peripherals could potentially use PCIe tunneling to read or write system memory directly, bypassing operating system security controls. While Thunderbolt 4 mandates Intel VT-d based DMA protection, USB4 implementations vary in their security implementations. Some budget implementations may lack adequate DMA protection, creating potential vulnerabilities.
Peripheral authentication presents another consideration. USB4's ability to connect high-performance storage and network devices increases the risk of malicious peripherals. Organizations handling sensitive data should evaluate USB4 security implementations carefully and consider Thunderbolt 4 for environments requiring guaranteed security features.
Compatibility challenges represent another significant consideration. While USB4 maintains backward compatibility with the massive installed base of USB devices, forward compatibility and optimal performance require attention to several factors:
- Cable Quality Variability: Not all USB-C cables support USB4 speeds or features, creating confusion and performance issues
- Implementation Inconsistency: Different manufacturers implement USB4 features differently, affecting compatibility
- Driver and Firmware Requirements: Optimal performance often requires updated drivers and firmware
- Resource Contention: Multiple high-bandwidth activities can create performance bottlenecks
- Thermal Management: Sustained high-performance operation requires adequate cooling
- Power Delivery Negotiation: Not all devices negotiate power delivery optimally, affecting charging performance
Common Implementation Issues and Mitigation Strategies
Users frequently encounter these USB4 implementation challenges:
- "Charging but Slowly" Syndrome: Devices charge but insufficiently during use, causing battery drain
Mitigation: Verify power delivery specifications and use certified high-wattage chargers - Intermittent Connectivity: Unstable connections with certain device combinations
Mitigation: Update all drivers and firmware, test with different cables - Display Recognition Issues: Monitors not detected or running at reduced resolutions
Mitigation: Check monitor compatibility, update display drivers, try different cables - Performance Inconsistency: Speed variations under different conditions
Mitigation: Ensure adequate cooling, avoid resource contention, use quality cables - Cable Length Limitations: 40Gbps speeds typically limited to 0.8m with passive cables
Mitigation: Use active cables for longer distances, accept reduced speeds if necessary
Many of these issues resolve with updated drivers, firmware, or better component matching. A systematic troubleshooting approach—starting with cable replacement, then driver updates, then component testing—solves most common problems.
Enterprise deployment considerations extend beyond individual device issues. Organizations must evaluate USB4 within their broader technology strategy:
Enterprise Deployment Considerations
For organizations, USB4 adoption involves strategic considerations beyond technical compatibility:
- Security Policy Alignment: Ensure USB4 implementations meet organizational security requirements
- Support Infrastructure: IT teams need training and tools for USB4 support and troubleshooting
- Asset Management: Track cables, docks, and accessories as organizational assets
- Standardization vs Flexibility: Balance the benefits of standardization with user flexibility needs
- Lifecycle Planning: Integrate USB4 into technology refresh cycles and budgeting
- User Education: Train users on proper USB4 usage, cable requirements, and troubleshooting
- Vendor Management: Establish relationships with reliable USB4 vendors and manufacturers
- Compliance Considerations: Ensure USB4 deployments meet industry-specific compliance requirements
Future-proofing considerations also warrant attention. While USB4 represents a significant advancement, technology continues evolving. USB4 Version 2.0 with higher bandwidth is already announced. Organizations and individuals should consider their investment timelines and whether current USB4 implementations will meet future needs. In many cases, USB4 40Gbps implementations provide adequate future-proofing for 3-5 year investment cycles, while 20Gbps implementations may have shorter useful lifespans as demands increase.
Environmental and sustainability considerations are increasingly important. USB4's potential to reduce electronic waste through universal compatibility and longer useful lifespans represents a significant benefit. However, the higher cost of quality USB4 components and the need for new cables during transition create short-term environmental impacts that must be balanced against long-term benefits.
Finally, managing expectations is crucial. USB4 delivers substantial improvements but isn't a panacea for all connectivity issues. Performance depends on multiple factors, and optimal results require attention to component quality, compatibility, and configuration. Educated users who understand these dependencies achieve better results than those expecting "magical" solutions.
10. Conclusion: The Connectivity Future
USB4 represents a pivotal moment in the evolution of digital connectivity—a convergence point where performance, simplicity, and universality align to create transformative possibilities. As we conclude this comprehensive analysis, several key themes emerge that define USB4's significance and future trajectory.
USB4 Technology Ecosystem: Complete Analysis Framework
USB4: THE FUTURE OF CONNECTIVITY - COMPLETE ANALYSIS
├── TECHNOLOGICAL FOUNDATION
│ ├── Built on Thunderbolt 3 protocol architecture
│ ├── Protocol tunneling for multiple data types
│ ├── Dynamic bandwidth allocation with QoS
│ ├── USB-C exclusive physical interface
│ └── Backward compatibility with massive USB ecosystem
├── PERFORMANCE ADVANTAGES
│ ├── Tiered implementation: 20Gbps baseline, 40Gbps premium
│ ├── Dual 4K display support or single 8K capability
│ ├── PCIe tunneling for external GPUs and high-speed storage
│ ├── USB Power Delivery 3.1 up to 240W
│ └── Intelligent resource management for multi-tasking
├── USER EXPERIENCE TRANSFORMATION
│ ├── Single-cable docking replaces multiple connections
│ ├── Simplified workspace setup and management
│ ├── Enhanced mobility and flexibility
│ ├── Reduced complexity for less technical users
│ └── Measurable productivity improvements (15-20 min daily savings)
├── MARKET DYNAMICS AND ADOPTION
│ ├── Flexible implementation creates market segmentation
│ ├── Premium devices adopt 40Gbps, mainstream uses 20Gbps
│ ├── Regulatory pressure (EU mandates) accelerates adoption
│ ├── Cable and accessory ecosystem growing rapidly
│ └── Consumer education challenge due to implementation variability
├── ECONOMIC CONSIDERATIONS
│ ├── Initial premiums decreasing with adoption (20-40% → 10-20%)
│ ├── Cable economy: $20-120 for certified cables
│ ├── Dock investments: $150-400 for full-featured solutions
│ ├── Total cost of ownership analysis essential
│ └── ROI varies by user type (professional vs casual)
├── THUNDERBOLT RELATIONSHIP
│ ├── Technological convergence with maintained distinction
│ ├── Thunderbolt: guaranteed features, premium positioning
│ ├── USB4: flexible implementation, universal adoption
│ ├── Asymmetric compatibility (Thunderbolt more inclusive)
│ └── Parallel evolution benefiting different market segments
├── INDUSTRY TRENDS AND FUTURE
│ ├── USB4 Version 2.0: 80-120 Gbps bandwidth
│ ├── Cross-industry adoption patterns varying by segment
│ ├── Wireless convergence as complementary technology
│ ├── AI-driven optimization in future implementations
│ └── Standardization efforts improving consistency
├── CONSUMER GUIDANCE FRAMEWORK
│ ├── User profile analysis for appropriate implementations
│ ├── Specification verification beyond marketing claims
│ ├── Compatibility testing before commitment
│ ├── Phased adoption strategies for organizations
│ └── Realistic expectations and systematic troubleshooting
├── RISKS AND CONSIDERATIONS
│ ├── Security considerations for DMA and peripheral risks
│ ├── Compatibility challenges requiring attention
│ ├── Common implementation issues and mitigation
│ ├── Enterprise deployment strategic considerations
│ └── Future-proofing within technology investment cycles
└── CONCLUSION AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
├── Transformative impact on connectivity simplicity
├── Enabler of new workspace paradigms and mobility
├── Foundation for next decade of connected experiences
├── Evolution toward truly universal standards
└── Balanced approach: performance + accessibility + sustainability
The USB4 Legacy: Simplicity Through Sophistication
USB4's most significant achievement may be its ability to make sophisticated technology simple. By intelligently managing complex protocol interactions behind a single, reversible connector, USB4 delivers professional-grade capabilities to mainstream users while maintaining the accessibility that has defined USB's success for decades. This balance between power and simplicity represents a maturing of connectivity technology—moving from a focus on raw specifications to holistic user experience.
The standard's flexible implementation approach, while creating some market complexity, ultimately serves diverse needs better than rigid one-size-fits-all solutions. Professionals can invest in full-featured implementations that guarantee performance, while mainstream users benefit from improved capabilities at accessible price points. This tiered approach reflects the reality of diverse user needs and budgets in a global market.
Looking forward, USB4 establishes a foundation that will support connectivity evolution for years. Its architecture accommodates increasing bandwidth demands, evolving display technologies, growing power requirements, and emerging use cases. The announced USB4 Version 2.0 demonstrates this forward compatibility, offering substantially increased performance while maintaining backward compatibility to protect investments.
As wireless technologies advance, USB4 and similar wired standards will evolve as complementary solutions rather than competitors—each serving appropriate use cases within an increasingly connected world. The physical connection will remain essential for reliability, security, and maximum performance even as wireless offers convenience for appropriate applications.
For consumers, businesses, and the technology industry, USB4 represents more than another specification update. It embodies a vision of connectivity that is simultaneously more powerful and more accessible—a vision where technology adapts to human needs rather than requiring humans to adapt to technology. This human-centric approach, combined with robust technical capabilities, positions USB4 not just as the present of connectivity, but as the foundation for its future.
The Path Forward: Recommendations for Stakeholders
As USB4 continues its adoption journey, different stakeholders have distinct roles in maximizing its benefits while addressing its challenges:
For Consumers and End Users
Educate yourself on USB4 implementations beyond marketing terms. Match your investment to actual needs rather than maximum specifications. Invest in quality certified cables and accessories. Test compatibility before committing to ecosystems. Maintain realistic expectations about performance and compatibility.
For Technology Manufacturers
Provide clear, detailed specifications rather than vague marketing claims. Participate in certification programs to ensure compatibility. Consider user experience in implementation decisions. Support the ecosystem with driver and firmware updates. Educate consumers about appropriate usage and expectations.
For Enterprise IT Organizations
Develop clear USB4 adoption strategies aligned with organizational needs. Establish standards for approved devices and accessories. Train support teams on USB4 troubleshooting. Implement phased adoption with proper testing. Balance security requirements with user productivity needs.
For Standards Organizations and Regulators
Continue improving certification and labeling for consumer clarity. Balance flexibility with consistency in specifications. Address security considerations in evolving standards. Consider environmental impacts in standard development. Foster industry collaboration while maintaining competition.
The collective efforts of these stakeholders will determine how successfully USB4 delivers on its promise of simpler, more powerful, more universal connectivity. With thoughtful implementation and educated adoption, USB4 can fulfill its potential as a transformative standard that benefits users across the spectrum from casual to professional.